Less Small kids Getting Immunizations: CDC
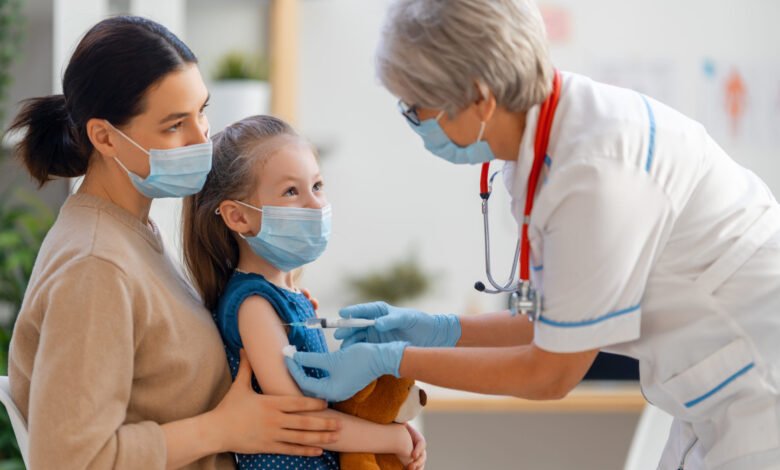

Less Small kids Getting Immunizations: CDC
In recent years, a troubling trend has emerged—fewer young children are receiving their recommended immunizations. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), this decline is causing significant concern among healthcare professionals and public health experts alike. Vaccinations play a critical role in protecting children from various preventable diseases, such as measles, mumps, and whooping cough. The reduction in immunization rates raises concerns about potential outbreaks of these and other dangerous illnesses.
- Understanding the Reasons for Decline
There are several factors contributing to this decrease in childhood immunization rates. One of the key reasons is vaccine misinformation. The rise of social media has provided a platform for false information regarding vaccines to spread rapidly. Some parents have become hesitant to vaccinate their children due to fears surrounding the safety and efficacy of vaccines, despite overwhelming scientific evidence proving their benefits.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has also played a role in the declining immunization rates. Many families delayed routine medical checkups during the pandemic due to concerns about exposure to the virus, resulting in missed vaccinations. Even after the height of the pandemic, some families have yet to catch up on their children’s immunization schedules.
- The Importance of Immunization
Immunizations are a fundamental part of keeping communities healthy. When a significant percentage of a population is vaccinated, herd immunity is established, reducing the chances of disease outbreaks. However, if vaccination rates continue to drop, herd immunity weakens, putting not only the unvaccinated but also vulnerable populations such as infants, elderly individuals, and those with compromised immune systems at risk.
The CDC emphasizes the importance of timely immunizations to avoid outbreaks of diseases that were once nearly eradicated. Measles, for example, saw a resurgence in the U.S. in recent years due to declining vaccination rates. This was particularly concerning because measles is highly contagious and can lead to severe complications, including pneumonia and encephalitis.
- Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy
To combat the declining immunization rates, it is crucial to address the issue of vaccine hesitancy. Public health campaigns must focus on educating parents about the importance of vaccines and dispelling the myths that surround them. Healthcare providers also play an essential role in this effort, as parents often trust their advice when it comes to their children’s health.
Furthermore, schools and community organizations can assist in promoting immunizations by providing resources and information to families. Offering convenient access to vaccines through school-based clinics or community health fairs may also encourage more parents to get their children vaccinated.
- Conclusion
The CDC’s findings on the decreasing immunization rates among young children highlight a concerning trend that requires immediate attention. Vaccinations are one of the most effective ways to protect children and the broader community from preventable diseases. By addressing the root causes of this decline and reinforcing the importance of vaccines, we can work toward ensuring that all children receive the protection they need to lead healthy lives.
